Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
Introduction to Machine Guarding
Machine guards are more than just protective barriers; they are the frontline defenders of workplace safety. By enclosing or shielding dangerous moving parts, machine guards prevent injuries like amputations, lacerations, and crushing incidents. Regulatory bodies such as OSHA mandate their use to create a secure working environment.
However, simply having guards in place isn’t enough. Without regular upkeep, even the most robust machine guards can fail. That’s why Maintaining Your Machine Guards is vital for every industrial operation.
Understanding Machine Guard Components
Machine guards come in various types, including fixed, interlocked, adjustable, and self-adjusting. Each type serves a specific function, depending on the machine’s operation and the level of hazard.
- Fixed Guards: Permanent fixtures for high-risk areas.
- Interlocked Guards: Disable machinery when the guard is removed.
- Adjustable Guards: Provide flexibility for various materials and sizes.
- Self-Adjusting Guards: Automatically adapt to the material being processed.
Materials such as steel, aluminum, and polycarbonate determine durability and ease of maintenance. Understanding these components helps in selecting the right maintenance approach.
Benefits of Proper Maintenance
Maintaining machine guards brings a wealth of advantages:
- Enhanced Safety: Reduces the risk of workplace injuries. A broken or dirty guard or shield will encourage workers to remove or bypass it.
- Increased Equipment Lifespan: Guards protect both workers and machinery, ensuring a longer lifespan for equipment.
- Reduced Downtime: Prevents production stoppages due to malfunctions.
- Cost Savings: Minimizes repair and replacement costs over time.
A small investment in routine care can yield significant returns in terms of safety and efficiency.
Common Machine Guard Issues
Over time, even high-quality guards can face:
- Wear and Tear: Constant exposure to operations causes degradation.
- Misalignment: Guards can shift, rendering them ineffective.
- Rust and Corrosion: This is especially prevalent in humid or chemically prone environments.
Being aware of these issues is the first step toward proactive maintenance.
One of the significant issues we observe is the degradation of polycarbonate over time. In fact, polycarbonate becomes translucent with age. Yellowing happens when polycarbonate is exposed to sunlight. For example, you have probably seen old car headlights that are translucent and yellowed due to exposure to UV radiation.
Machine oils and solvents can damage guard materials, degrading plastics and paint. Once a guard has been degraded enough, it will no longer protect people from stopping ejections.
Read more about polycarbonate environmental stress cracking here.
Routine Inspection Techniques
Regular inspections are key to effective guard maintenance:
- Daily Visual Checks: Look for noticeable signs of damage or misplacement. Encourage employees to be vigilant for potential issues.
- Weekly Operational Tests: Ensure interlocks and adjustable safety guards function properly.
- Monthly Detailed Reviews: Use a comprehensive checklist to inspect every part of the guard system.
Pro tip: Incorporate inspections into shift handovers to ensure consistency.
Cleaning and Lubrication Tips
A clean guard is a safe guard. Here’s how to do it right:
- Use mild detergents: Avoid harsh chemicals that degrade plastic or metal. Use a soft cloth and glass cleaner to keep the shields clean and maintain good visibility.
- Dry thoroughly: Moisture leads to rust.
- Apply lubricant where needed: Hinges, locks, and adjustable parts benefit from periodic lubrication.
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for cleaning agents and techniques.
When and How to Replace Worn Guards
Even with top-notch maintenance, guards wear out. Signs it’s time for replacement include:
- Visible cracks or holes
- Rust that won’t clean off
- Warping or distortion
Documentation and Record Keeping
Keeping track of maintenance ensures accountability:
- Use digital tools or simple spreadsheets.
- Record date, findings, and corrective actions.
- Review logs during audits or safety inspections.
Documentation builds a strong maintenance culture and supports compliance. I could not tell you the number of times that I saw machinery that had broken or disabled safety guarding. A proper maintenance plan will ensure that machine guarding remains in proper working order at all times.
Staff Training and Accountability
Empowered employees are the best defense against machine guard failures:
- Conduct monthly safety training.
- Rotate inspection responsibilities.
- Recognize and reward maintenance diligence.
When everyone feels responsible, maintenance becomes second nature.
Read more about machine shop safety for managers here.
A worker is more likely to remove a dirty, yellowed, or hard-to-see-through shield or guard. They might bypass safety interlocks or unscrew shields. To avoid this, please inform them of the process for obtaining a replacement shield.
Environmental Factors and Their Impact
Your maintenance schedule should factor in:
- Humidity Levels: Accelerates rust—use sealed guards.
- Chemical Exposure: Choose chemical-resistant materials.
- Temperature Extremes: Some plastics warp in heat—consider metal.
Adapting to your environment extends the longevity of your guard.
How often should machine guards be inspected? Daily visual checks and monthly detailed inspections are recommended. Please pay special attention to interlock switches to ensure they are functioning correctly.
Can I clean machine guards while the machine is running? No, always shut down the machine before cleaning or maintenance. Ensure you follow proper LOTO (Lockout, Tagout) procedures.
What are the signs of a failing safety guard? Cracks, rust, missing screws, or looseness. Inspect any plastics for microfractures or yellowing and replace them as needed.
What’s the best material for long-lasting guards? This depends on your environment. Use stainless steel for harsh environments and steel for applications that require a heavy-duty guard. High-impact resistant polycarbonate is an excellent choice for many applications.
Should maintenance logs be digital or paper-based? Either is acceptable, but digital offers better tracking and analytics.
Conclusion: Building a Culture of Guard Maintenance
Maintaining your machine guards is not just a technical task; it’s a mindset. By following these proven tips, you’ll boost performance, extend machine life, and most importantly, safeguard your team. Make maintenance a habit, not an afterthought.
We can help fix your safety guards.
Ferndale Safety can help you with:
On-Site Machine Safeguarding Assessments
Replacement of broken guards
Design and manufacture custom guarding and enclosures
Fill out the form, and one of our safety experts will get in touch with you shortly.
Learn More About Machine-Specific Safety
We have more articles that may interest you on safeguarding specific types of machinery.
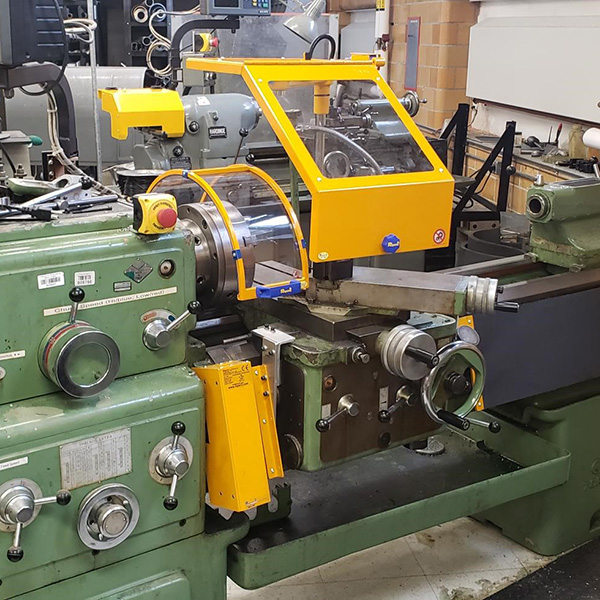

Find out how a lathe works and what can be done to increase lathe operator safety.
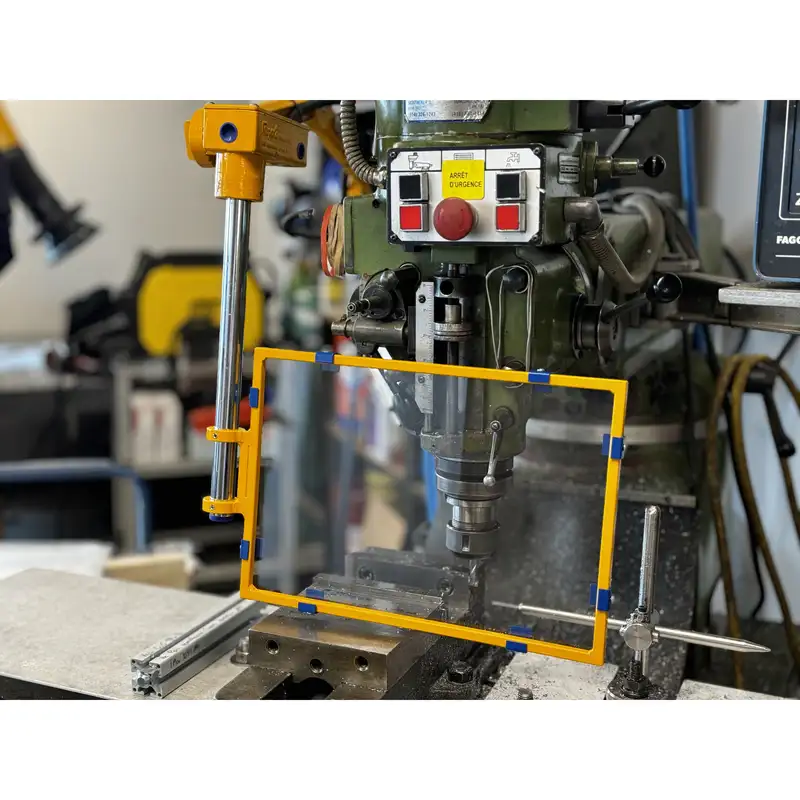
Learn about milling machines and how to safeguard them properly.

There is more to drill presses than you may think!
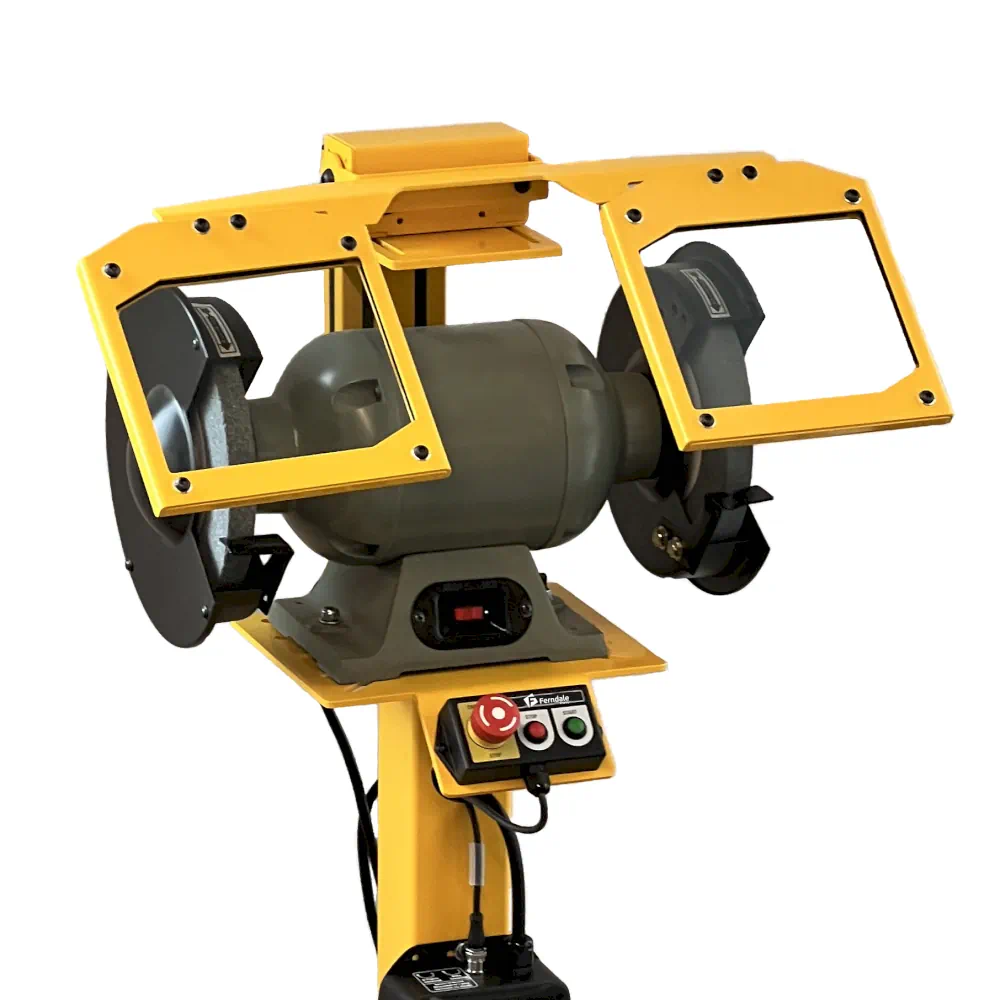

Did you know you should put anti-restart protection on your grinder?